
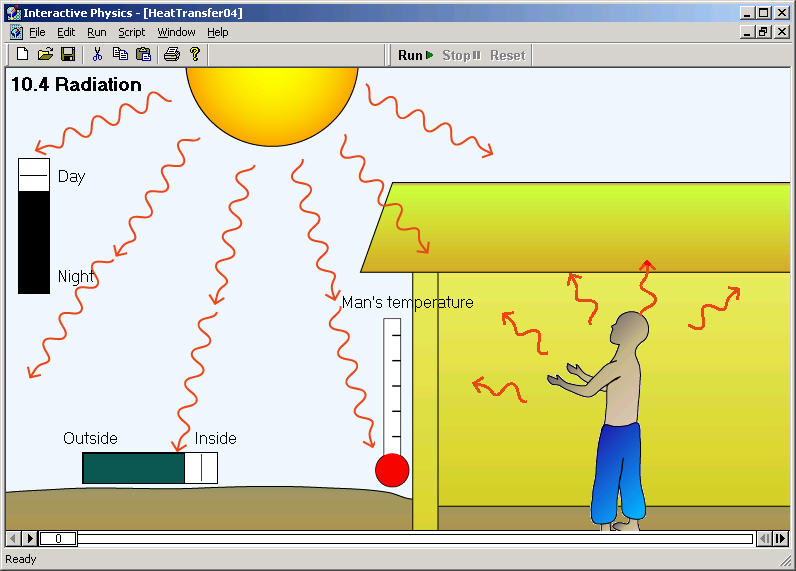

As sunlight enters the Earth system one of two different things can happen: it can either be absorbed or reflected. The majority of this light is in the visible spectrum. Most of the energy that passes through the upper atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface is in two forms, visible and infrared light. Energy is transferred from the sun to Earth via electromagnetic waves, or radiation. On the electromagnetic spectrum, it can be found between microwave radiation and visible light. You have probably seen a heat lamp warming food in a cafeteria the heat lamp is using one type of long-wave electromagnetic radiation, infrared infrared radiation: the long wave, electromagnetic radiation of radiant heat emitted by all hot objects. Radiation is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves.
RADIANT ENERGY EXAMPLES LICENSE
Reuse: This item is offered under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license You may reuse this item for non-commercial purposes as long as you provide attribution and offer any derivative works under a similar license. As you work through the these labs keep this relative scale in mind. The 1 mm line, that your pencil draws, represents the average thickness of the the first two layers of the atmosphere: the troposphere, the region of weather, and the stratosphere, which protects us from most of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.

This circle represents the Earth and the inner-most atmosphere. Use a compass to draw a circle with a radius of 127 mm. To get a sense of the thickness of the troposphere and stratosphere, two important layers of the atmosphere, try this simple exercise. When we look up at the sky from the ground, the atmosphere seems to go on forever, but in reality it is extremely thin when compared to the diameter of Earth. In the astronaut photograph at right, taken from the International Space Station, you can see the sun setting through the atmosphere. Energy from the sun heats Earth's surface, warms the atmosphere, provides energy for photosynthesis, causes evaporation, drives the weather and water cycles, and powers the ocean currents. × The profile of the atmosphere and a setting sun are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crew member on the International Space Station.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
